The official Visual Studio Code extension for Stylelint.
Table of Contents
You can install the extension from the Command Palette:
- Execute the
Extensions: Install Extensionscommand - Type
@id:stylelint.vscode-stylelintinto the search form - Install the topmost one with the verified publisher mark.
For more details, you can read the VS Code's extension installation guide.
You can disable VS Code's built-in linters either in the user or workspace settings.
For example, to disable the built-in CSS, Less, and SCSS linters:
"css.validate": false,
"less.validate": false,
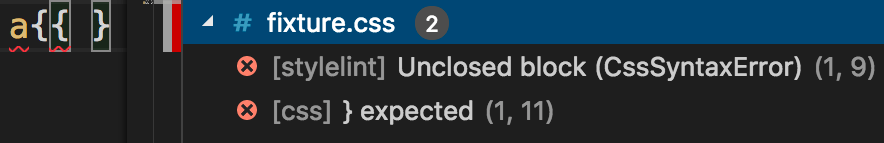
"scss.validate": falseAn example of duplicate error messages emitted by both the built-in linter and vscode-stylelint.
See the Stylelint getting started guide for more information.
The extension will automatically lint CSS and PostCSS documents (those with language identifiers css and postcss, respectively) once you create a Stylelint configuration file (or configure the Stylelint extension's settings) and install Stylelint.
You can see or change the current document's language in the bottom-right corner of the editor window.
You can use the stylelint.validate extension setting to lint additional languages.
For example, to additionally lint SCSS:
"stylelint.validate": ["css", "postcss", "scss"],Or to additionally lint CSS-in-JS in JSX and TSX:
"stylelint.validate": ["css", "postcss", "javascriptreact", "typescriptreact"],The extension first looks for a copy of Stylelint installed in the open workspace folder, then for a globally installed version if it can't find one. If neither can be found, it will not lint any documents.
The extension adds two commands to the command palette:
Fix all auto-fixable problems- apply fixes to all automatically fixable problemsRestart Stylelint Server- restart the Stylelint LSP and runtime server
The extension provides an action that you can use with VS Code's editor.codeActionsOnSave setting.
You can automatically fix all auto-fixable problems on save by setting the source.fixAll.stylelint property to explicit:
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.stylelint": "explicit"
}Or turn on auto fix for all providers, not just Stylelint:
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": "explicit"
}You can also selectively disable Stylelint:
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll": "explicit",
"source.fixAll.stylelint": "never"
}You can also selectively enable and disable specific languages using VS Code's language-scoped settings. For example, to disable codeActionsOnSave for HTML files, use the following:
"[html]": {
"editor.codeActionsOnSave": {
"source.fixAll.stylelint": "never"
}
}Though relying on a Stylelint configuration file in your project is highly recommended, you can instead use the following extension settings:
Type:
boolean
Default:true
Controls whether this extension is enabled or not.
Type:
"error" | "warn" | "info" | "debug"
Default:"info"
Controls the log level used by the Stylelint extension and language server. Restart the extension host or the window after changing the setting, since it's picked up at initialization.
Type:
string[]
Default:["css", "postcss"]
An array of language identifiers specifying which files to validate.
Type:
string[]
Default:["css", "postcss"]
An array of language identifiers specifying which files to enable snippets for.
Type:
string
Default:""
Used to supply a custom path to the Stylelint module.
Type:
"npm" | "yarn" | "pnpm"
Default:"npm"
Controls the package manager to be used to resolve the Stylelint library. This setting only has an effect if the Stylelint library is resolved globally. Valid values are "npm" or "yarn" or "pnpm".
Type:
object[]
Default:[]
An array of rule customizations that let you override the severity level of Stylelint rules. This is useful for downgrading errors to warnings, upgrading warnings to errors, or completely suppressing specific rules in the editor.
Each customization object has the following properties:
rule: A string pattern matching the rule name. Supports wildcards and negation patterns:- Exact match:
"color-named"matches only thecolor-namedrule. - Wildcard:
"color-*"matches all rules starting withcolor-. - Negation:
"!color-*"matches all rules except those starting withcolor-.
- Exact match:
severity: The severity level to apply."error": Show as error (red underline)."warn": Show as warning (yellow underline)."info": Show as information (blue underline)."off": Don't show the diagnostic."default": Use the original severity from Stylelint."downgrade": Convert errors to warnings, warnings to info messages."upgrade": Convert info to warnings, warnings to errors.
Customizations are applied in order, with later rules taking priority over earlier ones. This means that more general patterns should come before more specific ones for the specific rules to override the general ones.
Example:
{
"stylelint.rules.customizations": [
{
"rule": "font-*",
"severity": "info"
},
{
"rule": "!color-*",
"severity": "info"
},
{
"rule": "declaration-block-*",
"severity": "default"
},
{
"rule": "comment-word-disallowed-list",
"severity": "off"
},
{
"rule": "color-named",
"severity": "warn"
}
]
}Type:
Object
Default:null
Sets the Stylelint config option. Note that when this option is enabled, Stylelint doesn't load configuration files.
Type:
string
Default:""
Sets the Stylelint configFile option. Path to a JSON, YAML, or JS file that contains your configuration object. Use this option if you don't want Stylelint to search for a configuration file.
Type:
string
Default:""
Sets the Stylelint configBasedir option. The path to the directory to which relative paths defining "extends" and "plugins" are relative. Only necessary if these values are relative paths.
Type:
string
Default:""
Sets the Stylelint customSyntax option, which points to a PostCSS syntax module. Must be either the package name or an absolute path to the module.
e.g.
"stylelint.customSyntax": "sugarss"You can use ${workspaceFolder} to refer to the folder opened in VS Code.
e.g.
"stylelint.customSyntax": "${workspaceFolder}/custom-syntax.js"Type:
boolean
Default:false
Sets the Stylelint ignoreDisables option. If true, Stylelint ignores stylelint-disable (e.g. /* stylelint-disable block-no-empty */) comments.
Type:
boolean
Default:false
Sets the Stylelint reportDescriptionlessDisables option. If true, Stylelint reports stylelint-disable comments without a description.
Type:
boolean
Default:false
Sets the Stylelint reportNeedlessDisables option. If true, Stylelint reports errors for stylelint-disable comments that are not blocking a lint warning.
Type:
boolean
Default:false
Sets the Stylelint reportInvalidScopeDisables option. If true, Stylelint reports errors for stylelint-disable comments referring to rules that don't exist within the configuration object.
Migrating from previous major versions of the extension.
vscode-stylelint 2.x is the first version of the extension to support Stylelint 17.x. It's also backwards compatible with older version of Stylelint, down to 14.x.
It requires VS Code version 1.103.0 or later.
See also: Stylelint 14 migration guide
vscode-stylelint 1.x expects to use Stylelint 14 at minimum. Usage with prior versions of Stylelint is no longer supported. While older versions may continue to work for a while, you may encounter unexpected behaviour. You should upgrade your copy of Stylelint to version 14 or later for the best experience.
The syntax and configOverrides options have been removed from Stylelint 14 and this extension. See the following section for information on how to use different syntaxes.
Unlike 0.x, 1.x no longer provides a copy of Stylelint bundled with the extension. Bundling Stylelint brought up many unwanted side effects and significantly increased the extension's size.
Starting with 1.x, vscode-stylelint will depend on having a copy of Stylelint installed in the open workspace (recommended) or globally (not recommended). If the extension doesn't seem to be linting any documents, make sure you have Stylelint installed.
The 0.x versions of this extension, which used Stylelint 13.x and prior, supported validating many different languages out of the box without any additional configuration. However, this added a lot of complexity and resulted in many cases of unwanted or unexpected behaviour.
In current versions of the extension, the extension only supports validating CSS and PostCSS out of the box and requires additional configuration to validate other languages. You will need to:
-
Install the PostCSS syntax for the language you want to validate into your workspace, e.g. postcss-scss.
-
Configure Stylelint to use the syntax by providing the module name in the
customSyntaxoption using overrides (or use the corresponding option in this extension's settings).Example Stylelint config:
module.exports = { overrides: [ { files: ["**/*.scss"], customSyntax: "postcss-scss" } ] };
-
Add the language identifiers for the documents you want to validate to the extension's workspace or user settings using the
stylelint.validateoption.Example VS Code config:
{ "stylelint.validate": ["css", "scss"] }
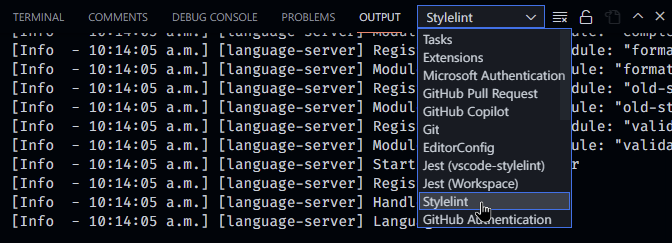
vscode-stylelint writes logs to the VS Code output panel:
You can enable more verbose log output by setting the logLevel extension setting or by running VS Code with the NODE_ENV environment variable set to development. You can do this on macOS and *nix by running:
NODE_ENV=development codeAnd on Windows by running:
cmd /C "set NODE_ENV=development&&code"Contributions are welcome! Please see the CONTRIBUTING.md file for details.